Competency #1
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is C.
![]()
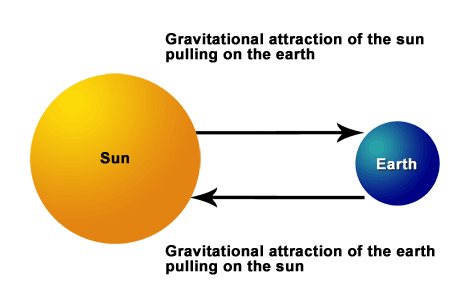
This is an example of Newton's third law - whenever an object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal but opposite in direction force on the first object.
That is to say, if the Sun pulls on the Earth, the Earth must pull on the Sun with the same force in an opposite direction.
Let's look at a drawing (not to scale)
Alternatively, you could use Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation to determine the size of the two forces.
| Gravitational Pull of Sun on Earth | Gravitational Pull of Earth on Sun | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| mass 1 (Sun): | 1.99x1030 kg | mass 1 (Earth) : | 5.98x1024 kg |
| mass 2 (Earth): | 5.98x1024 kg | mass 2 (Sun): | 1.99x1030 kg |
| Gravitational constant G: | 6.67x10-30 | G: | 6.67x10-34 |
| distance between sun and earth: | 1.55x1011 m | distance between earth and sun | 1.55x1011 m |
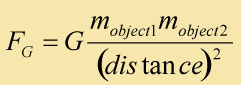 |
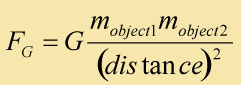 |
||
Fg = 6.67 x 10-34 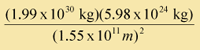 = 0.33 N (same either way) = 0.33 N (same either way) |
|||
In fact, without even using numerical values, we can see that the two forces are equal:
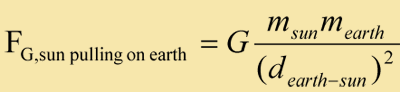
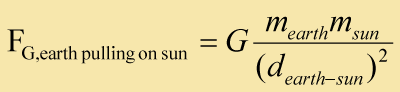
© 2008 Anne Arundel Community College