Competency #4
Answer and Explanation
![]()
Force Diagrams:
Force Diagrams:
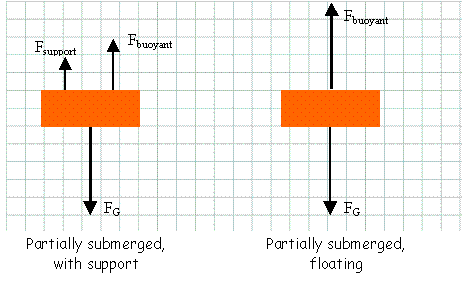
The arrow for the force of gravity, FG, is drawn the same length in each case, as the force of gravity depends only on the mass of the two objects (the orange block and the earth, in this case) and the distance between them (approximately equal to the radius of the earth), as per Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation.
For both objects, application of Newton's 2nd Law in the vertical direction, shows that the net vertical force must equal zero, since the vertical acceleration of each object is equal to zero.
For the floating object (on the right), the arrow for the buoyant force, Fbuoyant, is drawn the same size as the force of gravity since there are no other vertical forces acting and this is the only way to achieve a net vertical force of zero.
For the object on the left, the buoyant force, Fbuoyant, is drawn smaller than the force of gravity since there is another upward vertical force present.
For the object on the left, there is also a support force, Fsupport, present. For this object, the support force and the buoyant force combined are equal in magnitude to the force of gravity, and thus, the net force is zero. (Note: Based on the information given, it is not known whether the buoyant force is bigger than the support force, if the support force is bigger than the buoyant force, or if they are the same size. However, the sum of these two forces must equal the force of gravity.)
Also remember that Archimedes' Principle says that the buoyant force is equal to the weight of fluid displaced. Note that the object on the right is more submerged, has displaced more water, and thus has a greater buoyant force acting on it than the object on the left. This is reflected in the force diagrams, drawn above.