Competency #4
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is neither- the buoyant force acting on the block does not change, as long as it is fully submerged.
![]()
The block is shown below at two depths, with the arrows representing the size of the force on the sides of the cube.
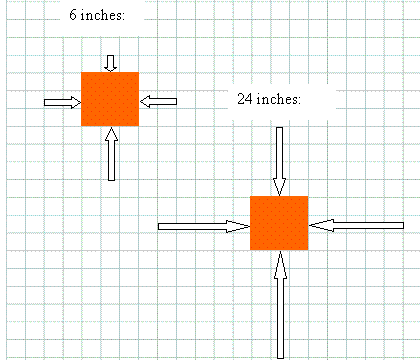
It is true that the pressure increases with depth. However, this does not change the buoyant force for a fully immersed object.
Remember that P = F/A. We can rearrange this to see that F = P * A. Since the area is the same on all 6 sides of the cube, we know that a larger pressure will lead to a larger force. Similarly, if the pressures on 2 sides are equal, then the forces are also equal.
Left to right : Let us first consider the sides. The force on the left is the same as the force on the right, but in the opposite direction, so there is no net force in this direction for the cube at either depth.
Front to back : Similarly, the force acting on the front of the block (into the screen; arrow not shown) is the same as the force acting on the back of the block (out of the screen; not shown), but in the opposite direction. Therefore there is a zero net force in this direction for both cubes.
Up and down : For the block 6 inches below the surface, the force acting upward is 3 N and the force acting downward is 1 N. Therefore the net force is 2 N upward. For the block at 24 inches below the surface, the force acting upward is 6 N and the force acting downward is 4 N. The net force is 2 N upward for this case also!
In fact, the net force would be 2 N upward for this block at any depth, as long as it is fully submerged (i.e. none of it is sticking out of the water).