Competency #5
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is C.
![]()
Recall that boron-10 can also be represented as 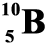 , indicating an atomic number of 5 (because there are 5 protons) and a mass number of 10 (5 protons + 5 neutrons). Similarly, boron-11 can be represented by
, indicating an atomic number of 5 (because there are 5 protons) and a mass number of 10 (5 protons + 5 neutrons). Similarly, boron-11 can be represented by ![]() , indicating an atomic number of 5 (because there are 5 protons) and a mass number of 11 (5 protons + 6 neutrons).
, indicating an atomic number of 5 (because there are 5 protons) and a mass number of 11 (5 protons + 6 neutrons).
- Average atomic mass = (10 + 11) / 2. This is a simple arithmetic average, but does not take into account that boron-11 is 4 times more abundant than boron-10.
- Average atomic mass = 11 (because it's the most common). The number below the symbol for each element on the periodic table is the average atomic mass. As you can see, this is usually a decimal number that is calculated by considering all of the naturally occurring isotopes for that element (not just the most common).
-
Average atomic mass = (20*10 + 80*11) / 100. The calculation shown above is correct! It uses a weighted average that takes into account the relative abundance of each isotope. This calculation is very similar to that used in the ‘Temperature and Mixing' lab when you were predicting the final temperature of a mixture of two containers of water. There are other ways to show this calculation that are equivalent to the one above:
Average atomic mass = 20/100*10 + 80/100*11
Average atomic mass = 0.20*10 + 0.80*11
Average atomic mass = 1/5*10 + 4/5*11
Though they may look a little different, they are doing the same calculation and will yield the same result.
- The average atomic mass cannot be found from the information given.
The information shown in the problem statement is the only information needed to make this calculation.
© 2008 Anne Arundel Community College