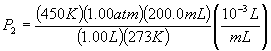
Combined Gas Law
Read Section 5.2 in the textbook.
The Combined Gas Law is P1V1 / T1 = P2V2 / T2 , where T is in Kelvin.
Note that Boyle's, Charles', and Amonton's Laws are all special cases of the Combined Gas Law:
Boyle's Law is
P1V1 = P2V2, which
is the Combined Gas Law when T is constant.
Charles' Law is
V1 / T1 = V2 / T2, which
is the Combined Gas Law when P is constant.
Amonton's Law is
P1 / T1 = P2 / T2, which
is the Combined Gas Law when V is constant.
We need to know how to use the Combined Gas Law, but we do not need to
memorize Boyle's, Charles', and Amonton's Laws :-)
Examples:
1. A 200.0 mL sample of gas at STP is heated to 177°C. At
this temperature the gas occupies a volume of 1.00 L. What is its pressure? (STP
means standard temperature & pressure, which is 0°C and 1 atm.)
First make a list of the given & what is to be found:
| V1 = 200.0 mL | V2 = 1.00 L |
| P1 = 1.00 atm | P2 = ? |
| T1 = 273 K | T2 = 177 °C + 273 = 450 K |
Then, recognizing that the Combined Gas Law will allow us to solve for the pressure, write this law and rearrange it to solve for P2.
P1V1 / T1 = P2V2 / T2 , in order to solve for P2, we must multiply both sides of the equation by T2/V2:
T2P1V1 / (V2T1) = T2 P2V2 / (V2T2)
T2P1V1 / (V2T1)
= T2 P2V2
/ (V2T2)
so, P2 = T2P1V1 / (V2T1)
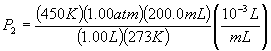
P2 = 0.330 atm
Note that it is necessary to write in the units to verify that they cancel
appropriately, and to show that suitable units for the answer are in the numerator.
2. A 250.0 mL sample of a gas at 78.0 cm Hg pressure is compressed at constant temperature until its pressure becomes 3.50 atm. What is its volume at this pressure?
First make a list of the given & what is to be found:
| V1 = 250.0 mL | V2 = ? |
| P1 = 78.0 cm Hg | P2 = 3.50 atm |
| T1 = T2 | |
Then, recognize that the Combined Gas Law simplifies to P1V1 = P2V2, since both sides of the Combined Gas Law can be multiplied by the same temperature, & temperature then cancels out. Now solve this equation for V2:
V2 = P1V1 / P2
![]()
V2 = 73.3 mL
3. A 4.00 L sample of a gas at 0°C is heated to room temperature, 25°C. It expands against the constant atmospheric pressure. What is its volume at room temperature?
First make a list of the given & what is to be found:
| V1 = | V2 = |
| T1 = | T2 = |
| P1 = | |
Be sure the temperatures are expressed in Kelvin.
What simplification of the Combined Gas Law is possible?
(Answer: Pressure factor cancels out.)
Solve the problem & check your answer.
Answer: V2 = 4.37 L
3. A sample of a gas at 23°C exhibits a pressure of 748 torr and occupies a volume of 10.2 L. Calculate the volume the gas will occupy if the temperature is increased to 30°C and the pressure is increased to 1.55 atm.
First make a list of the given & what is to be found:
| V1 = | V2 = |
| T1 = | T2 = |
| P1 = | P2 = |
Be sure the temperatures are expressed in Kelvin.
Are there any simplifications to the Combined Gas Law?
No.
Set up the problem and solve. Be sure to write units for all numbers. You will need a conversion factor.
Answer: 6.63 L